Laparoscopic/Keyhole Surgeries
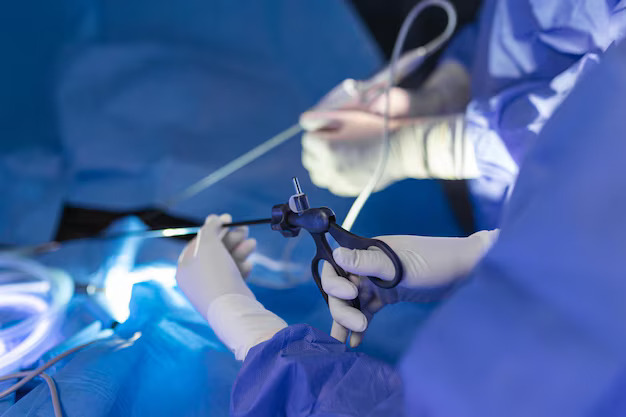
Laparoscopic, or keyhole surgeries, involve performing surgical procedures through small incisions using a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera and light. This minimally invasive approach allows surgeons to view and operate inside the body without making large cuts, leading to quicker recovery, reduced pain, and minimal scarring. Laparoscopic techniques are commonly used for a wide range of procedures across various medical specialties.
Why is Laparoscopic Surgery Done?
Laparoscopic surgery is performed for several reasons, including:
- Reduced Trauma: Small incisions result in less tissue damage and quicker healing.
- Faster Recovery: Patients often experience shorter hospital stays and a faster return to normal activities.
- Decreased Pain: Minimally invasive techniques generally result in less post-operative pain and discomfort.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Smaller incisions decrease the risk of infection compared to larger, open wounds.
- Improved Precision: Enhanced visualization and precision during surgery improve outcomes and reduce complications.
Who Requires Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery may be considered for individuals who meet the following criteria:
- Suitable Condition: Patients with conditions that can be effectively treated using laparoscopic techniques.
- Overall Health: Individuals who are in good overall health and able to tolerate surgery.
- Desire for Quick Recovery: Those who prefer a faster recovery and minimal scarring.
Treatment Surgery Options
There are several types of laparoscopic surgeries, including:
- Cholecystectomy: Removal of the gallbladder, commonly performed to treat gallstones and gallbladder disease.
- Appendectomy: Removal of the appendix, often performed in cases of appendicitis.
- Hernia Repair: Repair of hernias, such as inguinal or umbilical hernias, using small incisions.
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus, often performed for conditions such as fibroids, endometriosis, or cancer.
- Bariatric Surgery: Weight loss procedures, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, performed using laparoscopic techniques.
- Colorectal Surgery: Treatment of conditions such as diverticulitis, colorectal cancer, or inflammatory bowel disease.
Post-Operative Details
- Hospital Stay: Patients typically stay in the hospital for a shorter duration, often just a few hours to a couple of days, depending on the procedure.
- Dietary Changes: Depending on the surgery, patients may need to follow a specific diet, starting with liquids and gradually progressing to solid foods.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular follow-up visits are crucial to monitor recovery, ensure proper healing, and address any concerns.
- Physical Activity: Gradual increase in physical activity is recommended to aid recovery and improve overall health.
- Pain Management: Patients usually require less pain medication due to reduced surgical trauma, but pain management plans will be provided.
- Wound Care: Proper care of small incisions is necessary to prevent infection and ensure healing.
Laparoscopic surgery offers numerous benefits, including faster recovery, reduced pain, and minimal scarring. With advancements in surgical techniques and technology, patients can achieve effective treatment outcomes while minimizing the impact on their daily lives.
